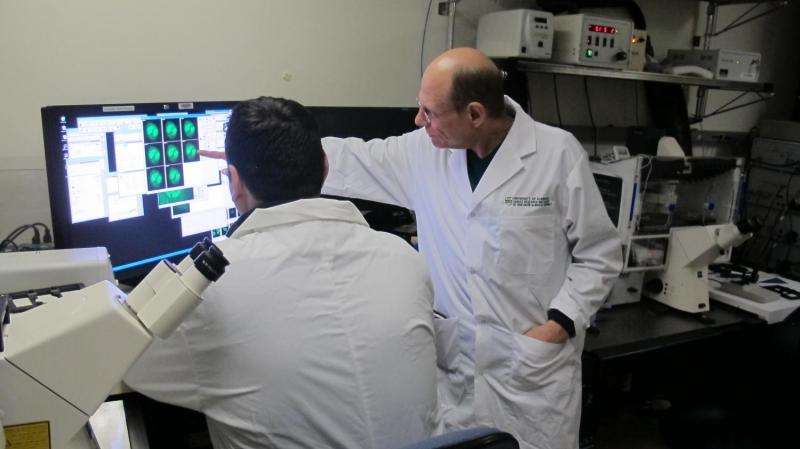
Stem cells to generate biological pacemakers?
Although today’s pacemakers are lifesaving electronic devices, they are limited by their artificial nature. For example, the devices require regular maintenance, must be replaced periodically, and can only approximate the natural regulation of a heartbeat. A new article highlights the promise and limitations of new methods based on stem cell and reprogramming technologies to generate biological pacemakers that might one day replace electronic pacemakers.
Can stem cell technology be harnessed to generate biological pacemakers?
Compromise Commercial Space Bill Passes House
Compromise Commercial Space Bill Passes House: Learn about House passage of the final version of H.R. 2262, the Commercial Space Launch Competitiveness Act, in November 2015, clearing the measure for the President.
Compromise Commercial Space Bill Passes House — Next Stop, the President
Salty solution to better, safer batteries
A team of researchers from the University of Maryland (UMD) and the U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL) have devised a groundbreaking “Water-in-Salt” aqueous Lithium ion battery technology that could provide power, efficiency and longevity comparable to today’s Lithium-ion batteries, but without the fire risk, poisonous chemicals and environmental hazards of current Lithium batteries.
Read more at: Salty solution to better, safer batteries
X-ray microscope reveals ‘solitons,’ a special type of magnetic wave
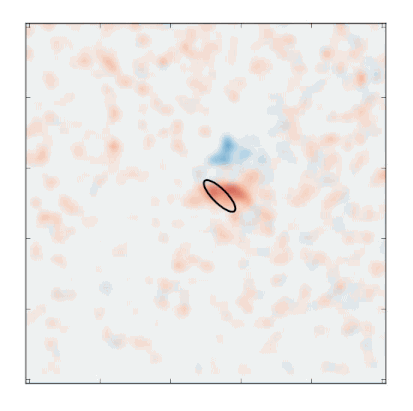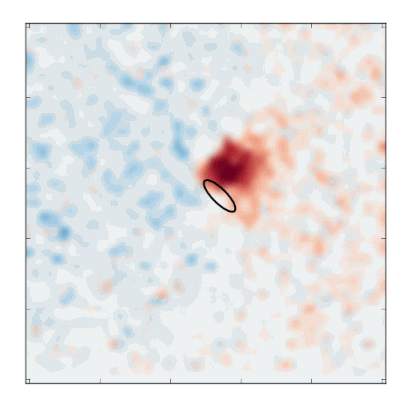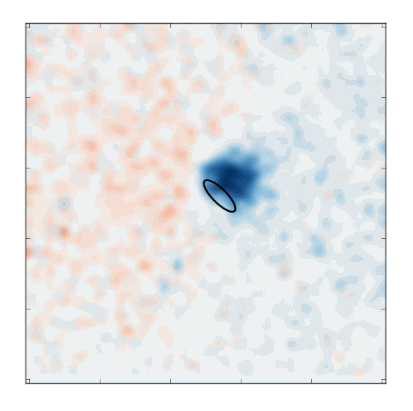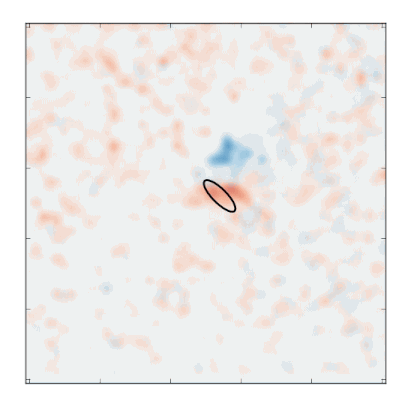
An ultrafast camera coupled to a custom-built X-ray microscope at SLAC’s Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource allowed researchers to produce a six-frame “movie” of the soliton’s motion. It took about 12 hours to record enough X-ray data to produce the movie. Credit: Stefano Bonetti/Stockholm University
X-ray microscope reveals ‘solitons,’ a special type of magnetic wave
History: Einstein was no lone genius.

Marcel Grossmann (left) and Michele Besso (right), university friends of Albert Einstein (centre), both made important contributions to general relativity.
Lesser-known and junior colleagues helped the great physicist to piece together his general theory of relativity, explain Michel Janssen and Jürgen Renn.
History: Einstein was no lone genius
Opening borders and barriers
An American physicist, a Japanese mathematician and a German cosmologist walk into a lab; what do you get? Based on recent outcomes, you’ll get ground-breaking science.
Opening borders and barriers : Nature : Nature Publishing Group
Molecule slows the clock on key aspects of aging in animals.
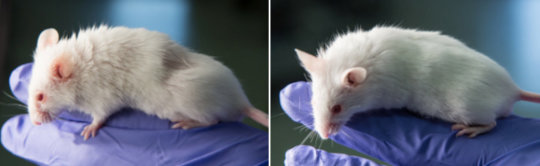
As mice age, those treated with J147 (right) showed improved physiology, memory and appearance that more closely resembled younger mice.
Scientists have discovered a molecule that slows the clock on key aspects of aging in animals.
Experimental drug targeting Alzheimer’s disease shows anti-aging effects: Molecule that slows the clock on key aspects of aging in animals.
The secret to safe DNA repair
Michael Hendzel knows all too well that there is little that people can do to control the stability of their genetic code. But he hopes his latest research will help impact this elusive and crucial aspect of medicine. Published in Nature Cell Biology, this research explores a previously unknown secret to DNA repair.
Fermi mission finds hints of gamma-ray cycle in an active galaxy
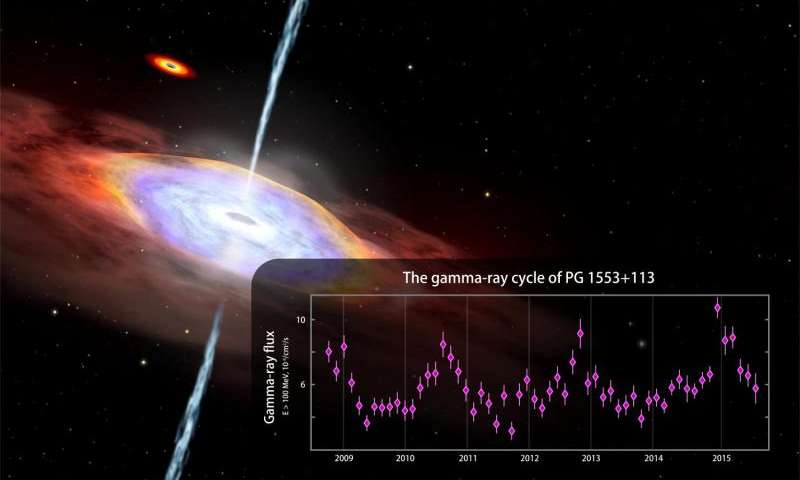
Astronomers using data from NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope have detected hints of periodic changes in the brightness of a so-called “active” galaxy, whose emissions are powered by a supersized black hole. If confirmed, the discovery would mark the first years-long cyclic gamma-ray emission ever detected from any galaxy, which could provide new insights into physical processes near the black hole.
Fermi mission finds hints of gamma-ray cycle in an active galaxy